Explore DeFi through decentralized exchanges
Now that we’ve explained everything DeFi, it’s time to become more familiar with decentralized exchanges (DEXs). On decentralized exchanges you can do the most of the features DeFi has to offer. Therefore we will discuss some platforms that have great DeFi integration and features. This is to show you what is out there, but no recommendation to use one specific. Use every platform at your own risk!
Examples of Decentralized Exchanges
Below are examples of Decentralized Exchanges, this is in no way a recommendation.
Notice that 3 out of 4 are called ‘Swap’ in the end? This is because the main feature you go do out there is swap one coin for another. You can also bridge and use many more products.
Why Decentralized Exchanges?
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are valued for their ability to facilitate peer-to-peer transactions without relying on intermediaries, providing users with greater control over their assets and enhancing security by eliminating the need for centralized authorities.
Examples of activities on a DEX
For the examples made, the Metamask (EVM) wallet will be used below. However, you can use any kind of hot wallet to interact with DeFi. Just keep in mind to never connect your cold storage to anything as it defeats the purpose of being your safe and cold storage. More security tips here. We will discuss:
Swapping Cryptocurrency
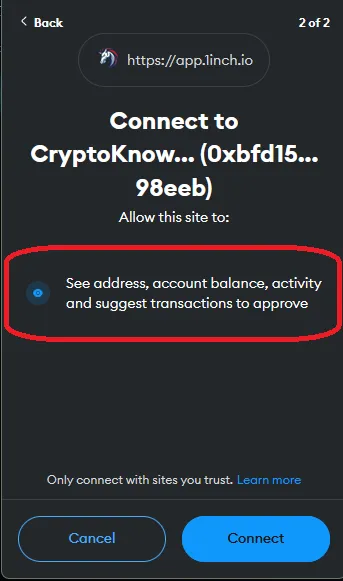
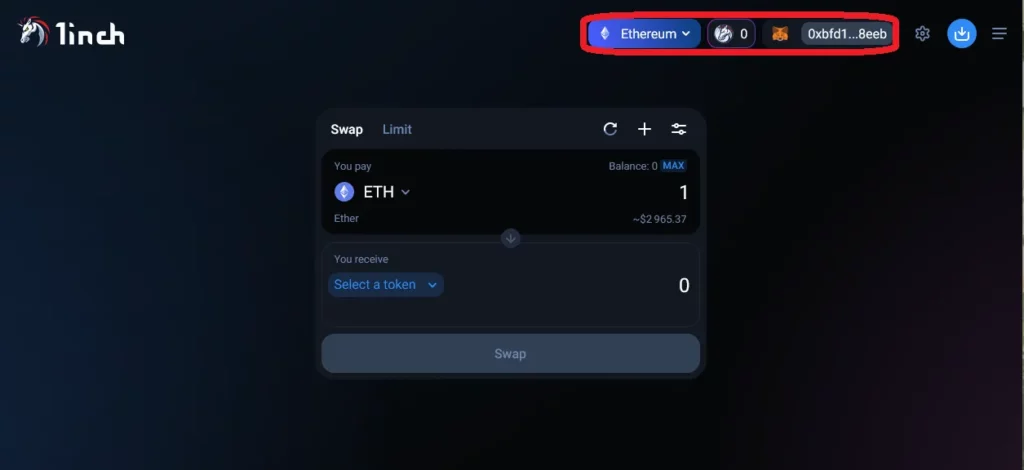
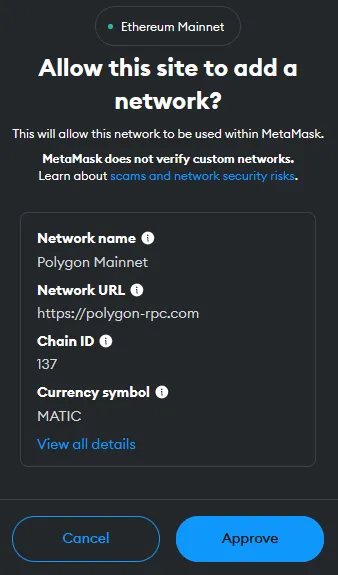
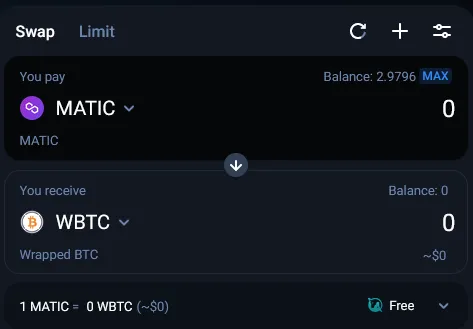
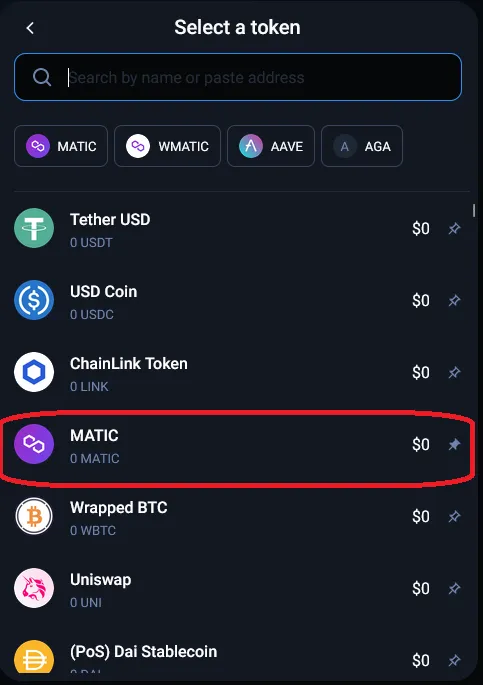
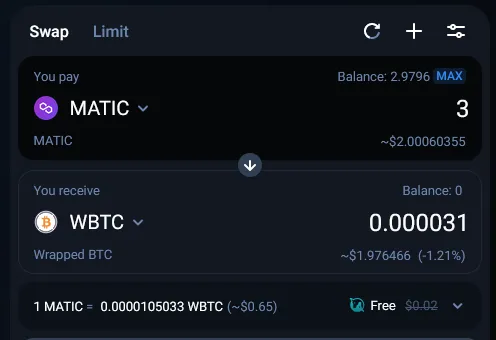
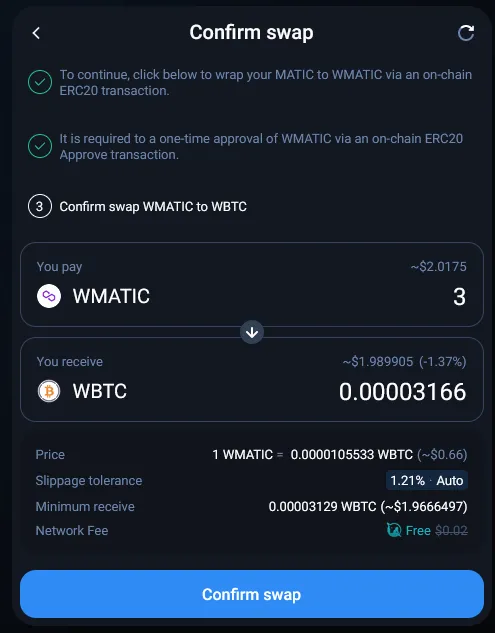
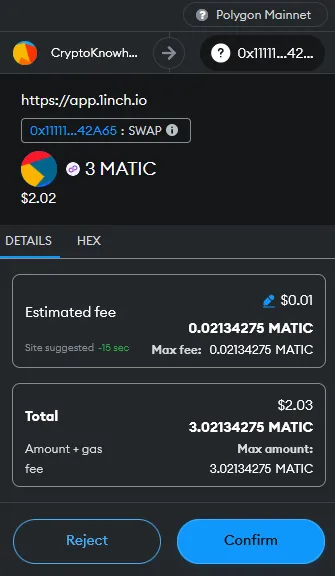
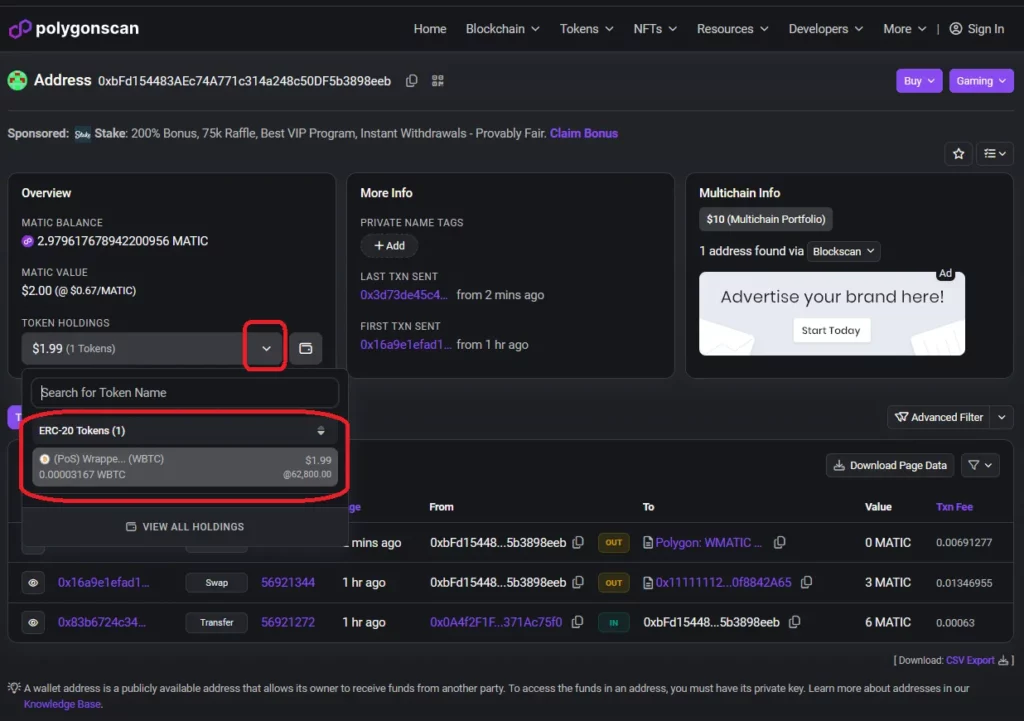
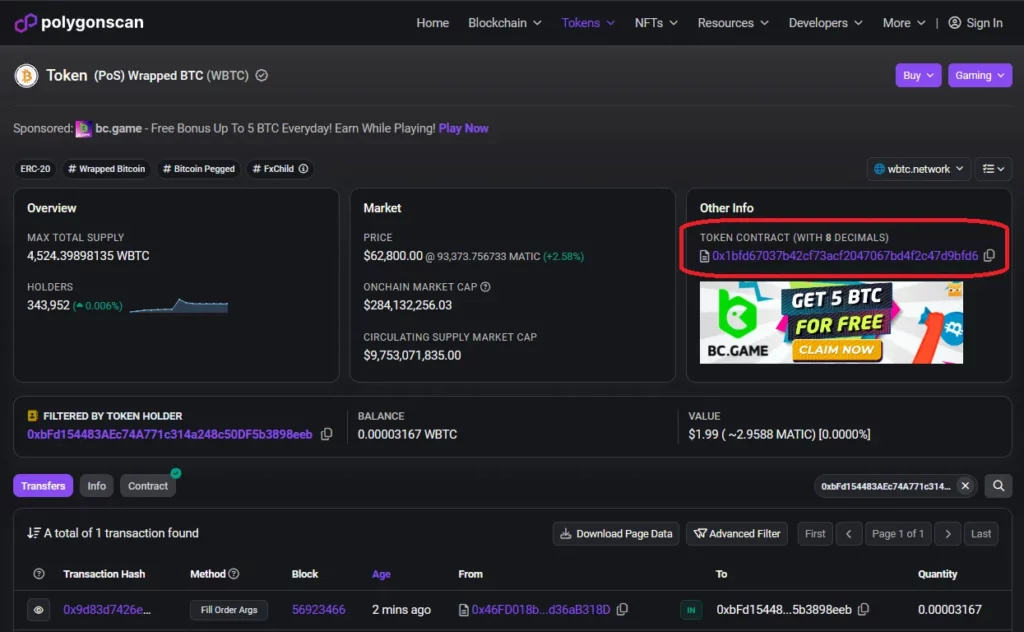
In this example, we are going to do a simple1 swap of 3 MATIC for WBTC (Wrapped Bitcoin) on 1inch. We are using the MetaMask wallet (browser extension) and we will be using the Polygon blockchain, a layer 2 scaling solution which means lower gas fees for us compared to the layer 1 Ethereum blockchain.
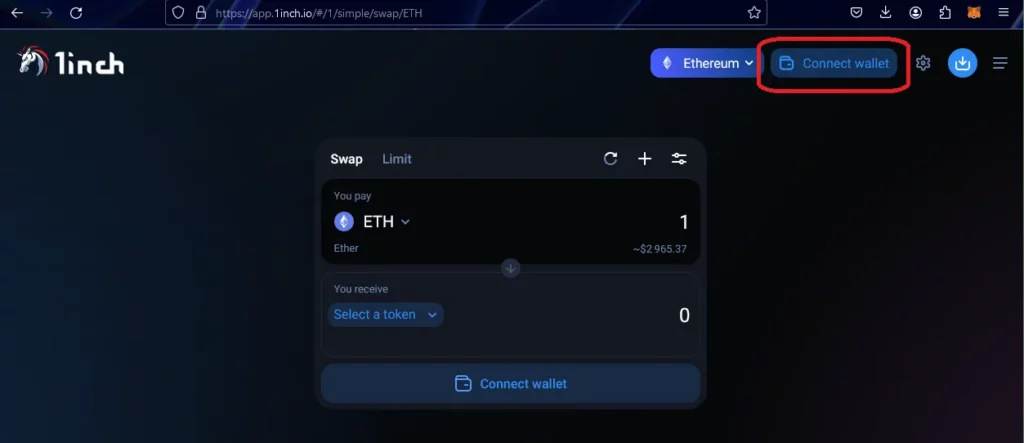
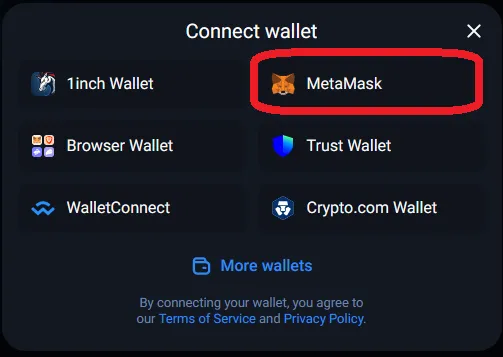


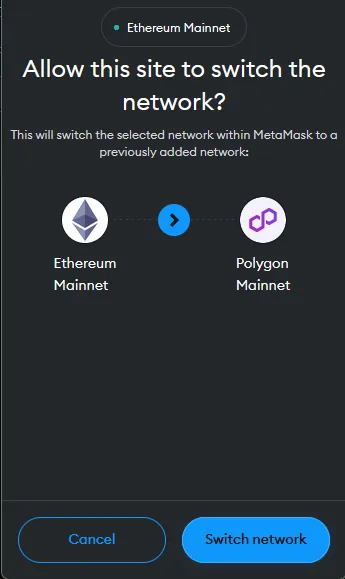
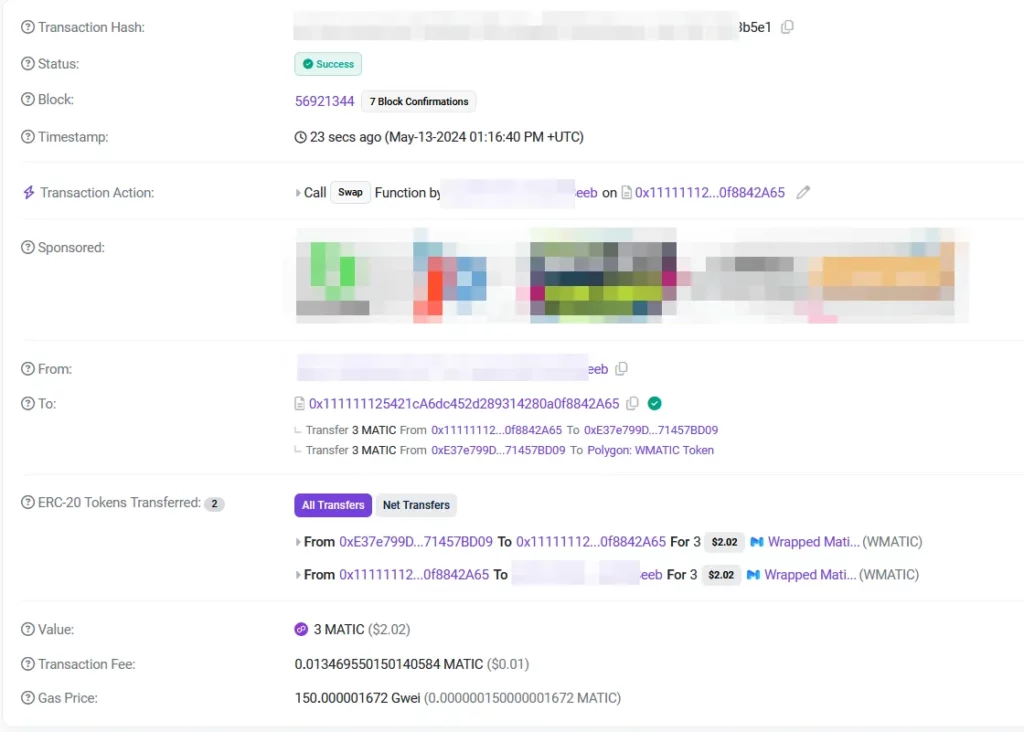
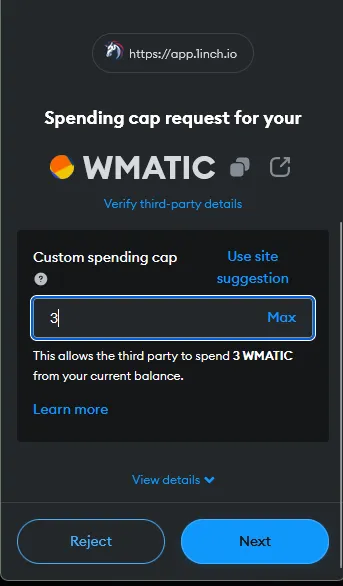
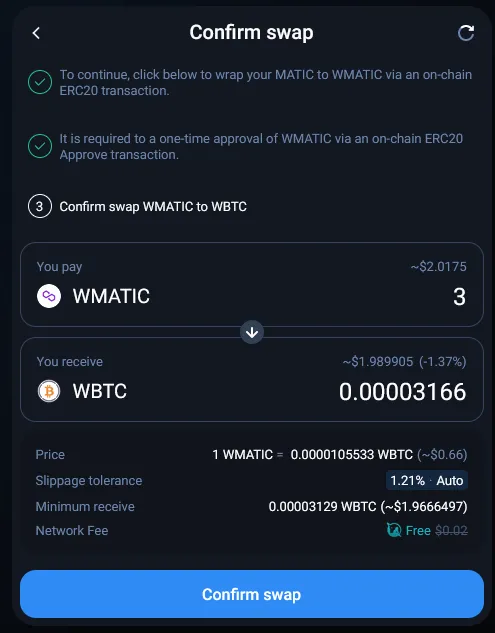
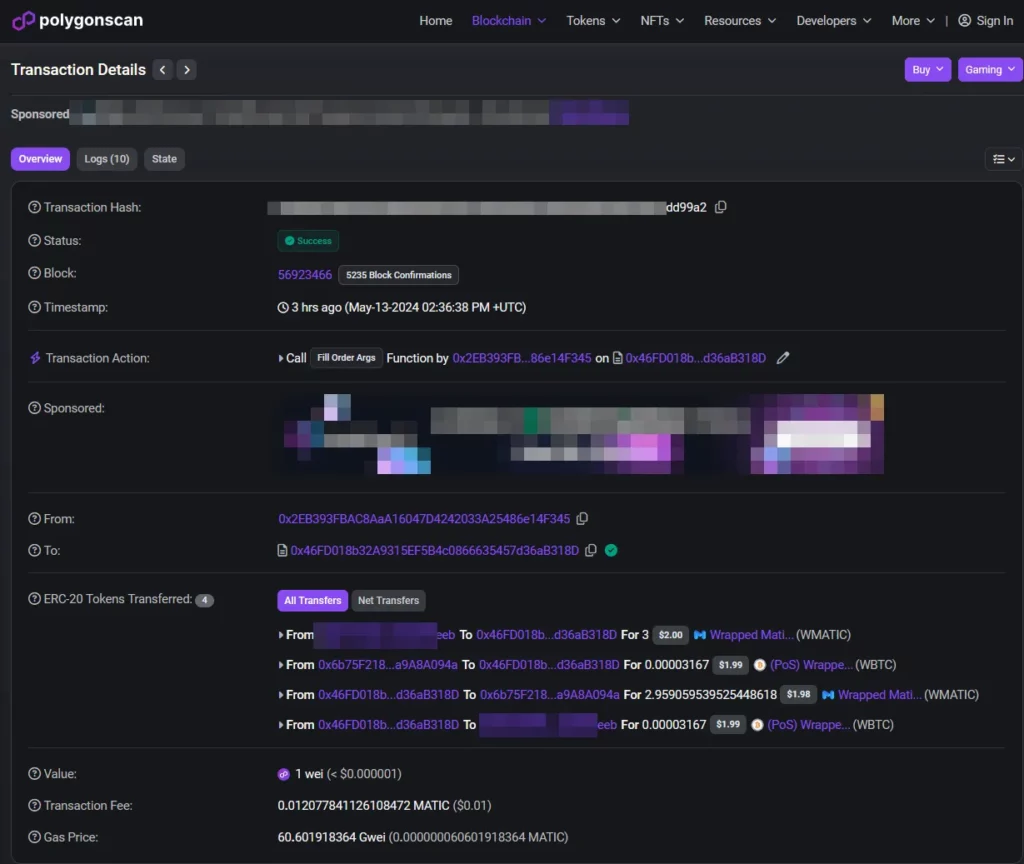
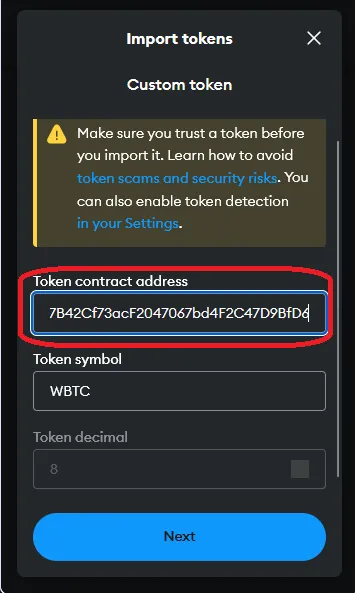
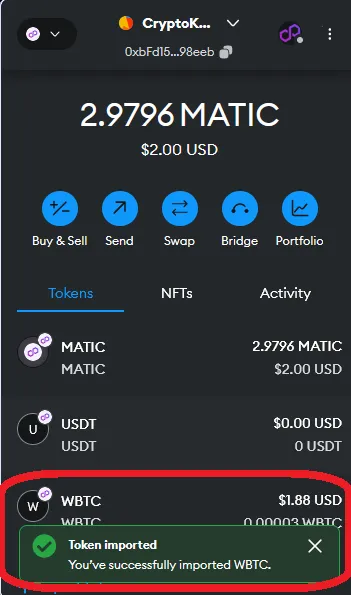
Bridging funds
You can use DEXs also for cross-chain transactions. Usually the native token of the decentralized exchange is used for bridging from one blockchain to another. For example on Pancakeswap, to bridge, you can select various blockchains, but only transfer CAKE tokens. CAKE is the token of Pancakeswap. But on destination chains you don’t always have the same token used for Gas.
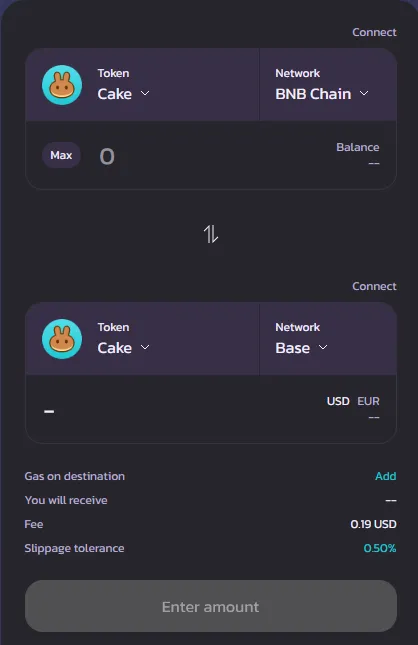
An example: We have BNB on the Binance Smart Chain, and we want to swap the BNB to ETH on the Base Blockchain. ETH is the native token on Base. So in this example I would swap my BNB to CAKE, to be able to use the bridge of Pancakeswap. Once swapped, I can now bridge the CAKE to Base. But, to interact with the CAKE on Base, I need ETH to pay for gas fees. So be careful how you bridge, and always make sure you have enough for gas fees to interact with your bridged tokens.
Providing liquidity
Liquidity providers are the backbone for Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs). They contribute crypto holdings to a pool, like for example ETH/WBTC, to facilitate trading between those tokens.
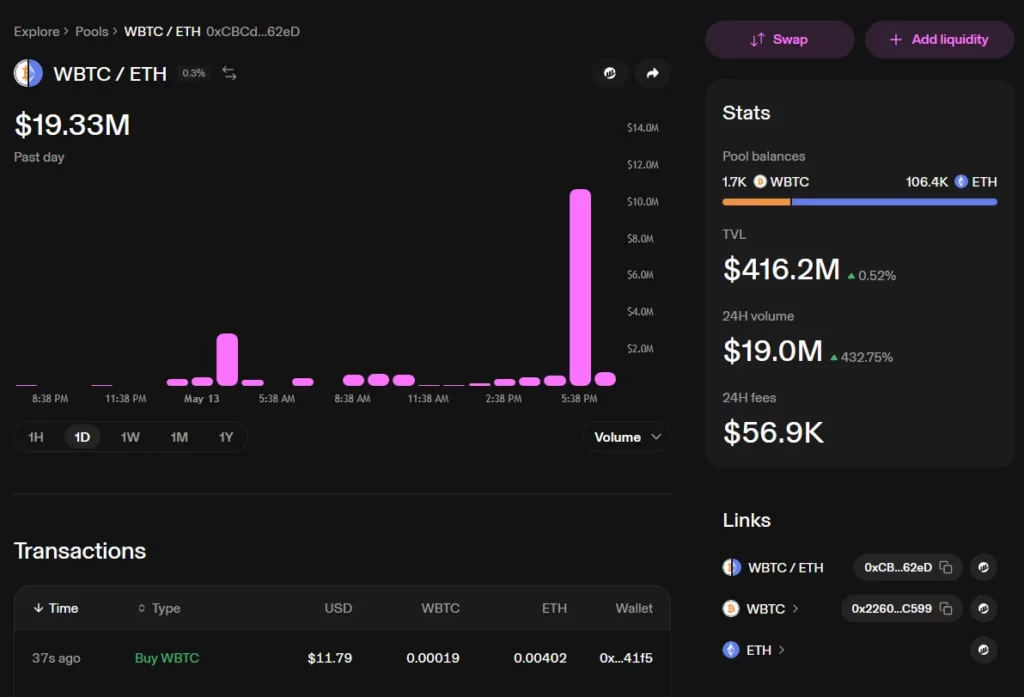
There’s a potential downside called impermanent loss. This occurs when the price of one token in the pool (say, WBTC) significantly increases compared to the other (ETH). While you hold equal value of both tokens in the pool, the ratio changes due to the price movement. If you withdraw your share from the pool at this point, you might end up with less WBTC (due to the price increase) even though its overall value went up. This is impermanent because if prices return to their original ratio, your loss disappears. But if the price divergence is permanent, you experience a real loss.
Staking
Staking involves locking up funds to support the network’s operations and validate transactions. You will earn rewards in return. DEXs utilize smart contracts and blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries. By staking your assets, you contribute to the security and stability of the decentralized network, fostering a more inclusive and transparent financial ecosystem. Benefits of staking on DEXs include earning passive income through staking rewards, actively participating in network governance decisions, and contributing to the decentralization of the ecosystem.
So liquidity providing involves supplying funds to liquidity pools on DEXs to facilitate trading pairs, earning fees from transactions. While staking typically involves locking up assets to secure the network. Liquidity providing offers more flexibility as funds can be withdrawn at any time, with staking you usually lock it for a fixed amount of time (e.g. 30 days).
Another big risk for liquidity providers is impermanent loss, which occurs when the value of assets in the pool changes relative to holding them outside the pool. Despite impermanent loss, liquidity providing remains a popular option if you look to earn passive income and contribute to the liquidity of decentralized markets.
That were only the basics..
There is so much more you can do with decentralized exchanges. Just explore what is out there by visiting various DEXs and their functionality.
- A simple swap because you can also swap with limit market orders, make perpetual orders, buy options, and more. But in the example used we used the most simplistic form of swapping. ↩︎




